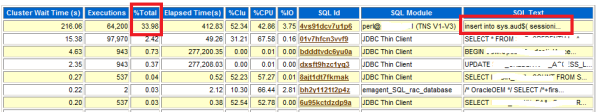
You show this (part of a) AWR report to the DBA and he proudly concludes: disable auditing, it is killing the performance! And thus, quite often Oracle database auditing is not enabled. And here are the 3 main reasons why auditing is not turned on:
– DBAs, developers, etc. are not familiar with this feature: For those who are not familiar with auditing.
– Security is not considered important and necessary: For those who do not consider auditing important, I wish them luck. They are anyway not interested in what I have to say..
– Performance is being hit by enabling auditing: For the ones having issues with performance when auditing is enabled, here is something.
There are 3 major reasons why performance suffers when auditing is enabled: too much is being audited, AUD$ still hangs in the SYSTEM tablespace and surprise, surprise: the Oracle bugs.
1. Too much is being audited. If it is a new database, spend some time with all parties involved on what to audit. The reality however is something like that: go-live day is getting closer, oh do we have auditing enabled? How do you enable it, can you give me the command please. And it should not go like that. You first decide on the value of audit_trail and then audit what is really needed, do not audit repetitive commands that generate too many inserts into the AUD$ table for it can grow very fast indeed.
If it is an existing database, check first what is being audited. To find out system audited stuff run the following:
select * from DBA_PRIV_AUDIT_OPTS |
select * from DBA_STMT_AUDIT_OPTS; |
Note that the difference between the two views above is very small and I have not found yet a place with explanation about the difference. The documentation says that DBA_STMT_AUDIT_OPTS describes the current system auditing options across the system and by user while DBA_PRIV_AUDIT_OPTS describes the current system privileges being audited across the system and by user. Puzzled? Me too.
For example, AUDIT SYSTEM belongs only to DBA_PRIV_AUDIT_OPTS while PROFILE, PUBLIC SYNONYM, DATABASE LINK, SYSTEM AUDIT, SYSTEM GRANT and ROLE belong only to DBA_STMT_AUDIT_OPTS.
On the other hand, CREATE PUBLIC DATABASE LINK, EXEMPT ACCESS POLICY, CREATE EXTERNAL JOB, DROP USER and ALTER DATABASE belong to both views, get it 
For the auditing options on all objects, check DBA_OBJ_AUDIT_OPTS.
2. AUD$ still hangs in the SYSTEM tablespace. The system tablespace might be fragmented. Starting 11gR2, Oracle supports moving the AUD$ table out of the SYSTEM tablespace. But first, noaudit your policy or stop the auditing.
If still running 11.1.0 or a below, here is how to do it:
create tablespace AUDIT_DATA datafile ...; |
create table AUDX tablespace AUDIT_DATA as select * from AUD$; |
create index i_aud2 on AUD$(sessionid, ses$tid) tablespace AUDIT_DATA; |
Remember to purge the records on regular basis. Do not just delete them but move them to a centralized auditing repository. Use the new DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT package. C In urgent cases, it is safe to run truncate table AUD$;
If you use FGA, remember to move also FGA_LOG$ away from the SYSTEM tablespace:
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.set_audit_trail_location( |
audit_trail_type => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD, |
audit_trail_location_value => 'AUDIT_DATA'); |
3. Oracle bugs. If you enable auditing you might get several bugs for free, most old ones should be fixed in 11.2.0.2, don’t know about the new ones 
